
This story originally appeared on 05.20.16
Dr. Frances Oldham Kelsey had only been with the Food and Drug Administration for about a month when she was tasked with reviewing a drug named thalidomide for distribution in America.
Marketed as a sedative for pregnant women, thalidomide was already available in Canada, Germany, and several African countries. It could have been a very simple approval. But for Kelsey, something didn’t sit right. There were no tests showing thalidomide was safe for human use, particularly during pregnancy.
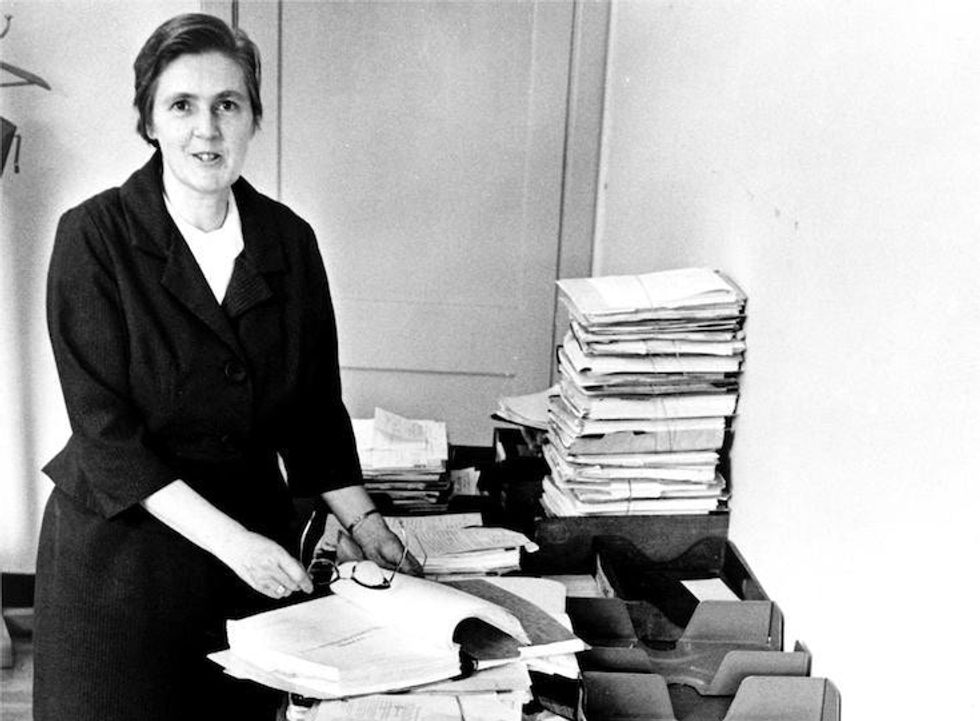

Kelsey in her office at the FDA in 1960. Image by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
When Chemie Grünenthal released thalidomide in West Germany years earlier, they called it a “wonder drug” for pregnant women. They promised it would treat anxiety, insomnia, tension, and morning sickness and help pregnant women sleep.
What they didn’t advertise were its side effects.
Because it crosses the placental barrier between fetus and mother, thalidomide causes devastating — often fatal — physical defects. During the five years it was on the market, an estimated 10,000 babies globally were born with thalidomide-caused defects. Only about 60% lived past their first birthday.
In 1961, the health effects of thalidomide weren’t well-known. Only a few studies in the U.K. and Germany were starting to connect the dots between babies born with physical defects and the medication their mothers had taken while pregnant.
At the outset, that wasn’t what concerned Kelsey. She’d looked at the testimonials in the submission and found them “too glowing for the support in the way of clinical back up.” She pressed the American manufacturer, Cincinnati’s William S. Merrell Company, to share research on how their drug affected human patients. They refused. Instead they complained to her superiors for holding up the approval. Still, she refused to back down.
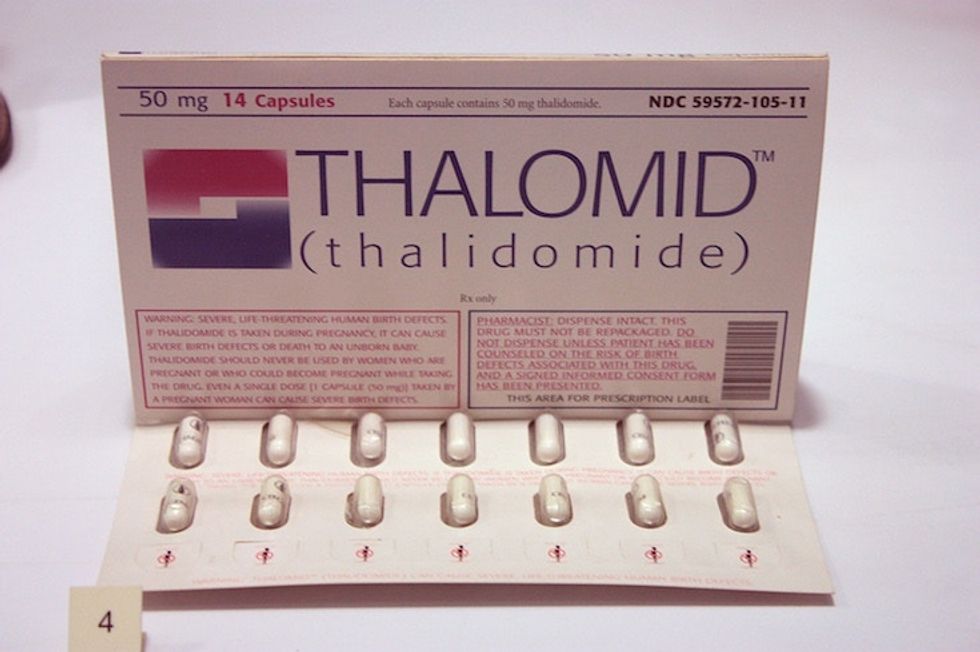
A sample pack of thalidomide sent to doctors in the U.K. While more than 10,000 babies worldwide were born with thalidomide-related birth defects, FDA historian John Swann credits Dr. Kelsey with limiting the number of American babies affected to just 17. Image by Stephen C. Dickson/Wikimedia Commons.
Over the next year, the manufacturer would resubmit its application to sell thalidomide six times. Each time, Kelsey asked for more research. Each time, they refused.
By 1961, thousands of mothers were giving birth to babies with shocking and heartbreaking birth defects. Taking thalidomide early in their pregnancy was the one thing connecting them. The drug was quickly pulled from shelves, vanishing mostly by 1962.
Through dogged persistence, Kelsey and her team had prevented a national tragedy.
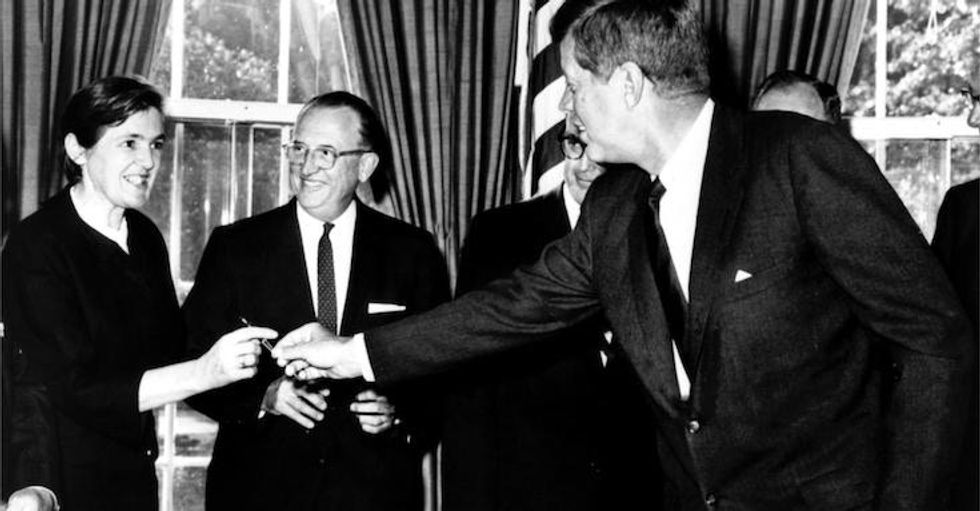

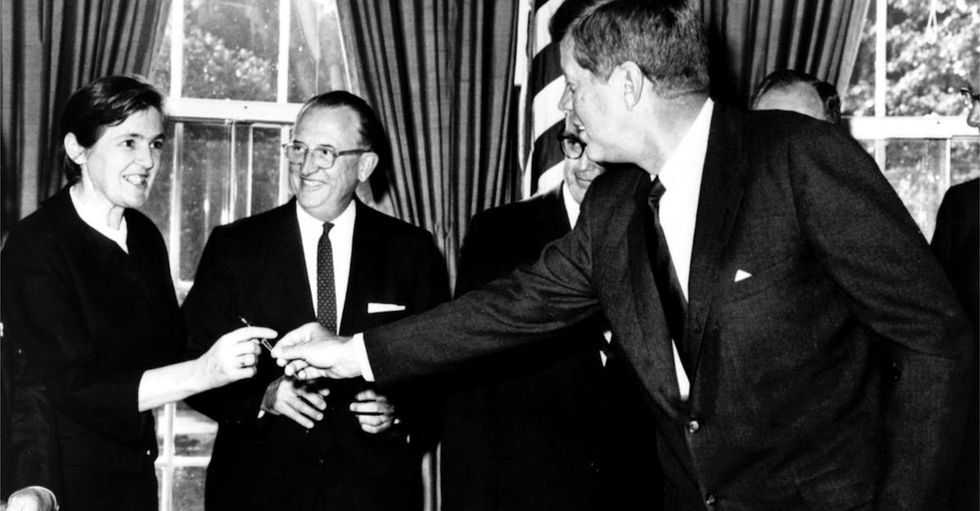
Kelsey joins President John F. Kennedy at the signing of a new bill expanding the authority of the FDA in 1962. Image by the United States Food and Drug Administration.
In 1962, President John F. Kennedy honored Kelsey with the Federal Civilian Service Medal. He thanked her for her exceptional judgment and for preventing a major tragedy of birth deformities in the United States:
“I know that we are all most indebted to Dr. Kelsey. The relationship and the hopes that all of us have for our children, I think, indicate to Dr. Kelsey, I am sure, how important her work is and those who labor with her to protect our families. So, Doctor, I know you know how much the country appreciates what you have done.”
But, she wasn’t done yet. Later that year, the FDA approved new, tougher regulations for companies seeking drug approval, inspired in large part by Kelsey’s work on thalidomide.
Reached via email, FDA historian John Swann said this about Kelsey’s legacy: “[Her] actions also made abundantly clear to the nation the important public health role that drug regulation and FDA itself play in public health. The revelation of the global experience with that drug and America’s close call indeed provided impetus to secure passage of a comprehensive drug regulation bill that had been more or less floundering during the time FDA was considering the application.”
Kelsey continued to work for the FDA until 2005. She died in 2015, aged 101, just days after receiving the Order of Canada for her work on thalidomide.
Bureaucratic approval work is rarely thrilling and not often celebrated. That’s a shame because it’s so critical.
People like Kelsey, who place public health and safety above all else — including their career — deserve every ounce of our collective respect and admiration.
