It’s unfortunate that humans are wired to notice everything bad going on in the world and to ignore the things that are going right. Our collective negativity bias was illustrated in a 2016 survey that asked people in 17 countries “Do you think the world is getting better or worse, or neither getting better nor worse?”
Fifty‐eight percent of respondents thought that the world is getting worse, and 30% said that it is doing neither. Only 11% thought that things are getting better.
However, there is a wealth of data to support the idea that the world is only improving when it comes to the hallmarks of human progress: education, freedom, poverty and health.
In a recent interview with Upworthy, Chelsea Follett, the managing editor at Human Progress, explained why humans have a bias toward negativity, and the media isn’t doing us any favors.
“Historically, obviously our ancestors in a primitive environment who overreacted to danger were more likely to survive than those who underreacted,” Follett told Upworthy. “But there is a point where unwarranted panic can actually be detrimental to your survival if you abandon policies or institutions that are actually working, or that have allowed you to make tremendous progress in the past.
“There’s also the nature of the media,” she added. “Obviously sudden, noteworthy and rare events are the ones that make headlines, whereas long-term slow, steady, incremental progress is just not as interesting.”
Our World in Data, an organization that performs “research and data to make progress against the world’s largest problems” has created a revealing document that shows just how far humanity has come over the past 200 years. The graphs show how life has changed for a random sampling of 100 people over the past two centuries.
The graph covers six topics that are cornerstones of human progress: poverty, basic education, literacy, democracy, vaccination and child mortality.
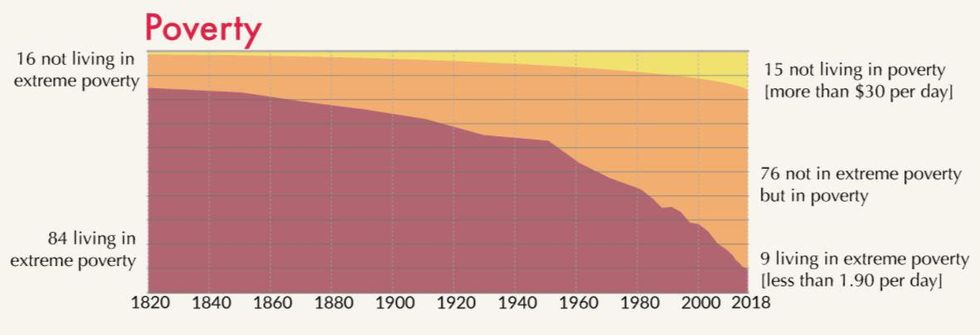
Poverty
In 1820, 84 out of 100 people lived in extreme poverty, and over 200 years that number has dropped more than nine times to just 9 in 100. “The headline could be ‘The number of people in extreme poverty fell by 130,000 since yesterday’ and they wouldn’t have this headline once, but every single day since 1990, since, on average, there were 130,000 people fewer in extreme poverty every day,” Our World in Data wrote.
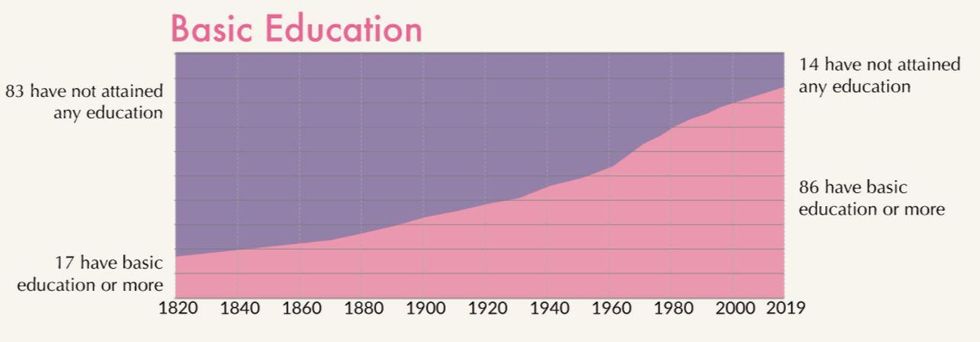
Basic Education
Two hundred years ago, 83 out of 100 people had no education at all. That number has been reduced to just 14 over the past 200 years.
Our World In Data says that number is only going to get better. “Focusing on the educational breakdown the projection suggests that by 2100, there will be almost no one without formal education and there will be more than 7 billion minds who will have received at least secondary education,” Our World in Data said.
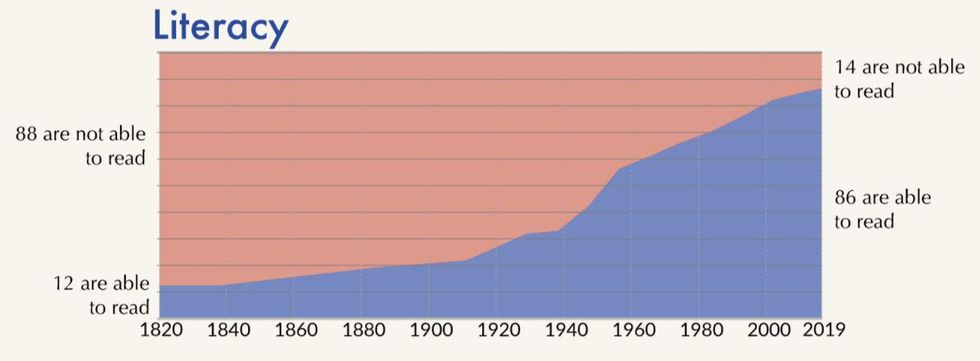
Literacy
In 1820, only 12 people out of 100 could read. In 2019, that number has risen more than seven times to 86. These numbers will continue to rise because a large portion of the world’s illiterate population is older.
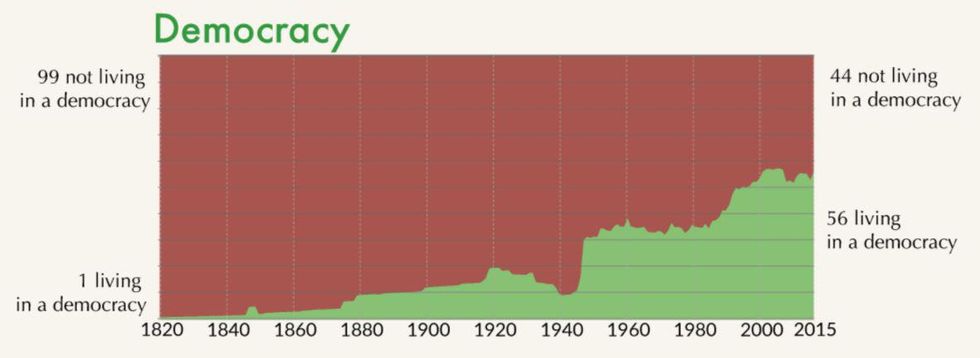
Democracy
Only 1 out of 100 people lived in a democracy back in 1820. Now, 56 out of 100 people live in a country where they can select their elected officials. This was a big change that came after World War II.
“In the second half of the 20th century, the world has changed significantly: Colonial empires ended, and more and more countries turned democratic,” Our World in Data wrote. “The share of the world population living in democracies increased continuously–particularly important was the breakdown of the Soviet Union which allowed more countries to democratize.”
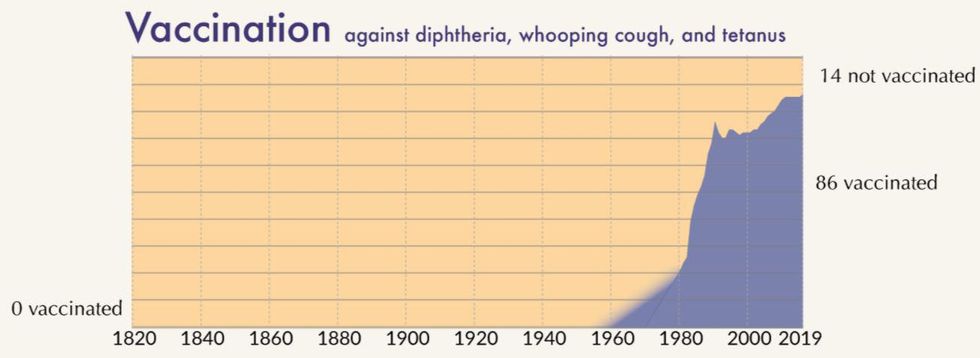
Vaccination
Over the past 60 years, the number of people out of 100 that would have been vaccinated against diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus has risen from 0 to 86.
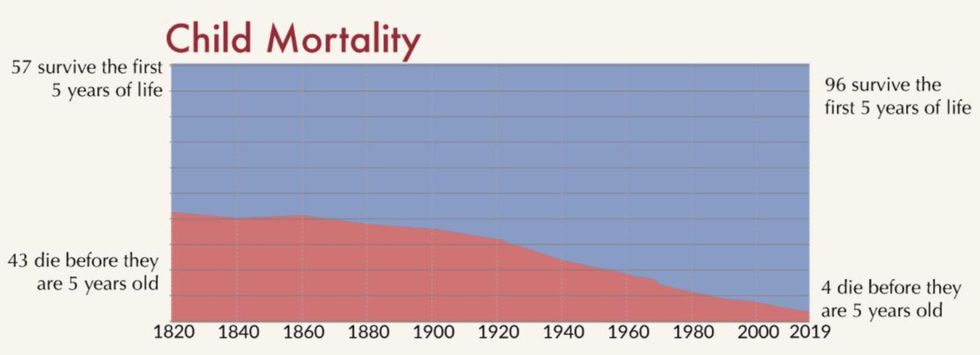
Child Mortality
Can you imagine living at a time when almost half of all children born never lived to kindergarten age? “In 1800 the health conditions were such that around 43% of the world’s newborns died before their 5th birthday,” Our World In Data wrote. “In 2017 child mortality was down to 3.9% – 10-fold lower than 2 centuries ago.”