
The negative effects of climate change are all around us—countless devastating heatwaves, droughts so severe in some areas that long lost ancient relics have reappeared, and in other areas, extreme storms destroy entire communities.
With all the visible decline on our planet, improvements might not be so obvious. But they do exist. All we need to do is look up.
Euro News announced on Sept. 19 that the Earth’s ozone layer, nature’s shield against UV radiation from the sun, has made significant progress against prior damage.
This is not only some much-needed relief against an onslaught of bad news for the environment, it also shows us that a better future is possible with concentrated effort.
It’s been 37 years since researcher Jonathan Shanklin first discovered a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica. His findings instigated arguably the biggest environmental movement of the 1980s, leading to the universally ratified Montreal Protocol, which phased out human-made, ozone-depleting chemicals (aka chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs, remember those?) previously found in cleaning products, certain appliances and hairspray—just imagine how much hairspray was probably being used during that time to create the signature ’80s coif … yikes.

Increased UV radiation can lead to more cases of skin cancer, cataracts and impaired immune systems. It is also believed to be contributing to the increase in melanoma, the most fatal of all skin cancers. And it’s worth noting, since 1990, the risk of developing melanoma has more than doubled.
Though the potential danger of CFCs had been discovered as early as the mid-’70s, it would take a giant scare like a big gaping chasm in the sky for folks to really pay attention. But pretty soon it was a full-blown, mass hysteria sensation. One environmentalist even compared it to “AIDS from the sky” back in 1991.
Fast forward to 2022, and a new study from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows that the overall concentration of those damaging chemicals has dropped just over 50%, back to levels not seen since before 1980.
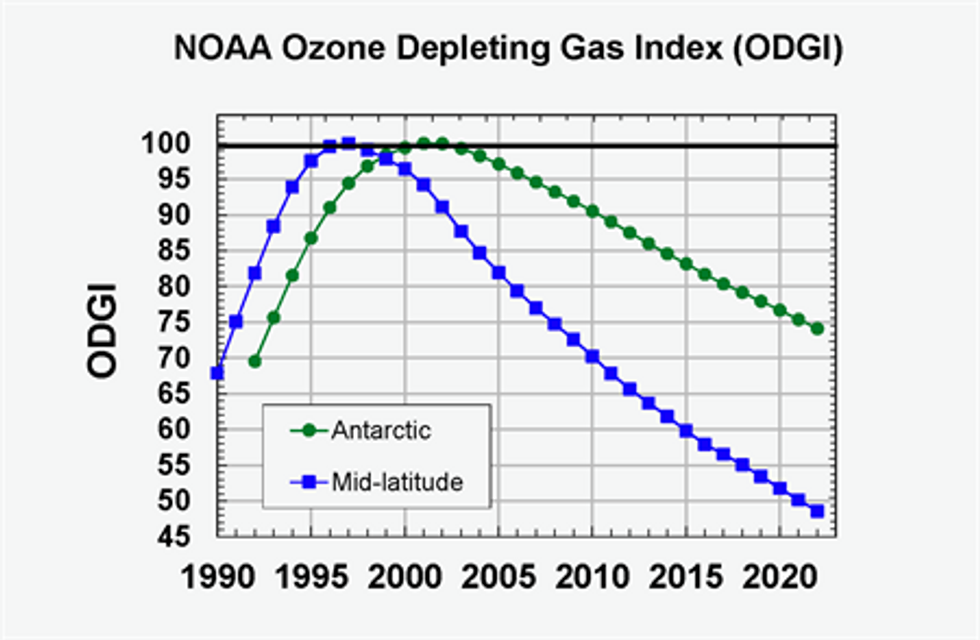
Of course, progress doesn’t mean perfection. Antarctica, which still experiences a large hole once a year, has seen a slower pace of reduction. But even still, chemicals have fallen 26%, the report revealed. And until it does close, the hole is being closely monitored using 3D imaging.
The Montreal Protocol has been a success in part because it forced corporations to come up with alternative solutions. Today we have plenty of brands that are environmentally conscious, but that wasn’t always the case. And lo and behold, a huge systemic shift caused a huge positive impact.
We still only have one planet to call our home and it will take a collective effort to protect it, just as it did to damage it. It can be easy to get nihilistic (or at the very least, anxious) when only the destruction is visible. That’s why it’s important to acknowledge and celebrate the small victories—it helps us hold onto hope and leads to more inspired action. Because, as we can see, for good or for bad, every action counts.
