
These days, the name Albert Einstein is basically a synonym for “genius.”
Einstein’s theory of relativity is one of the cornerstones of modern physics and his predictions continue to be confirmed today, even over a hundred years later. That’s not to mention his famous E=mc2 equation and the nuclear weapons it eventually helped spawn (which Einstein came to deeply regret).
He could even be pretty wise at times. A note scrawled with a piece of advice — “A calm and modest life brings more happiness than the pursuit of success combined with constant restlessness.” — recently sold for $1.56 million.
But there’s a different reason Einstein was amazing that many people might not realize: He was also a fervent civil rights activist.
Though his life ultimately came to be full of fame and fortune, Einstein wasn’t a stranger to prejudice.
Einstein was Jewish, living in Germany as Hitler rose to power. Einstein despaired over the Nazi’s anti-Semitism and became an outspoken critic of the Nazi party, which only drew more attacks against him. Major newspapers published attack pieces against him. His house was raided while he was away. He even appeared on a pamphlet list of the enemies of Nazi Germany. The caption below his picture read, “Not Yet Hanged.”
The harassment would ultimately prove to be too much. In 1933, Einstein abandoned his home and job at the Prussian Academy and sailed to the United States, stating: “I shall live in a land where political freedom, tolerance, and equality of all citizens reign.”
Though the United States proved to be a haven for Einstein for the rest of his life, he must have been disappointed to see his newly adopted country fail to live up to the promise of equality.
At the time, the United States was still deeply segregated and Jim Crow laws severely restricted the rights of black Americans. Even Princeton, the college that’d become Einstein’s workplace, wouldn’t admit black students. Einstein could see the parallels, and, just as he refused to be quiet in Germany, so too in the United States.
Over the next decades, Einstein would become a staunch defender and ally of both the civil rights movement and the men and women who fueled it.
When opera star Marian Anderson was denied a hotel room because of her skin color, Einstein opened his house to her. He worked with actor and singer Paul Robeson on the American Crusade Against Lynching and invited him to perform at Princeton when the singer was blacklisted. He publicly encouraged the NAACP and W.E B. Du Bois for years and appeared as a character witness when the federal government tried to indict the man.
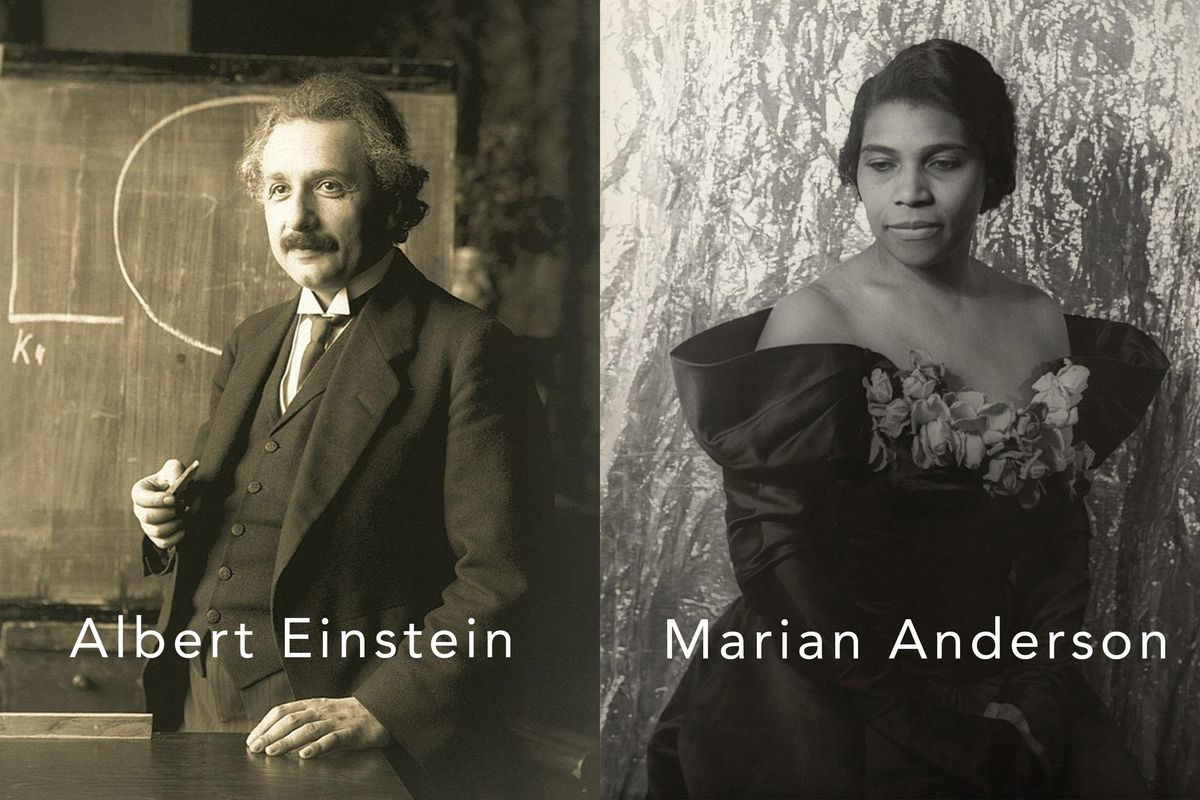
In 1946, he published an essay for white readers about racial bias in Pageant magazine, writing:
“Your ancestors dragged these black people from their homes by force; and in the white man’s quest for wealth and an easy life they have been ruthlessly suppressed and exploited, degraded into slavery. The modern prejudice against Negroes is the result of the desire to maintain this unworthy condition. …
I do not believe there is a way in which this deeply entrenched evil can be quickly healed. But until this goal is reached there is no greater satisfaction for a just and well-meaning person than the knowledge that he has devoted his best energies to the service of the good cause.”
That same year, he gave a speech at Lincoln University calling racism was “a disease of white people.” He also added, “I do not intend to be quiet about it.”
Einstein was clearly one of the greatest minds of the 20th century. But perhaps what made him a truly special human being wasn’t just that he was smart, or that he was funny, or that he left behind a lot of great anecdotes (and notes for bellboys).
Perhaps it was that he used that magnificent brain of his to not just understand the world, but to try to make it more just, fair, and peaceful place.
This article originally appeared on 10.27.17
